The Circulatory System
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels located on each side of the neck. Their role is to supply oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain.
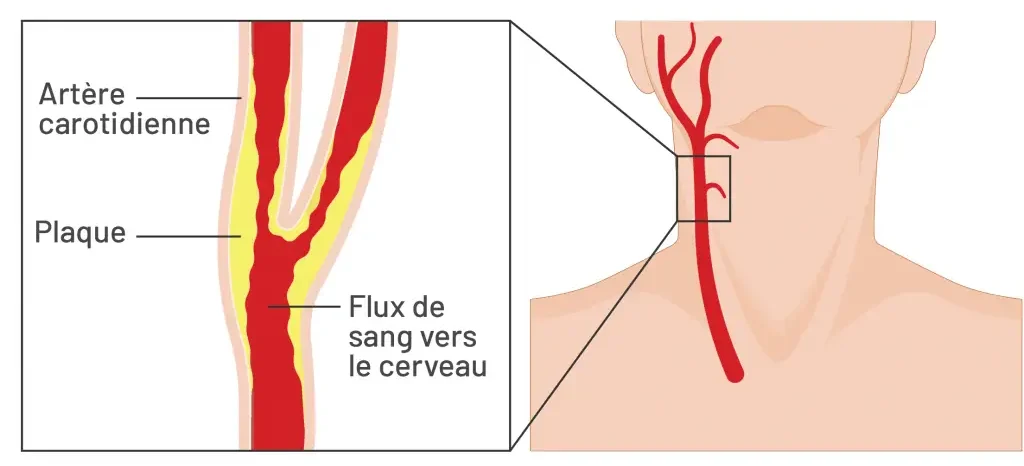
When these arteries become narrowed due to plaque buildup, blood flow to the brain is reduced. This condition is known as carotid stenosis and significantly increases the risk of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) and stroke.
Early detection is essential, as carotid stenosis often develops silently without noticeable symptoms.
What Is Carotid Stenosis?
Carotid stenosis is the narrowing of one or both carotid arteries, most commonly caused by atherosclerosis — the accumulation of fatty deposits (plaque) along artery walls.
As plaque builds up:
- Blood flow becomes restricted
- Small clots or plaque fragments may travel to the brain
- The risk of stroke increases significantly
Carotid stenosis is a serious vascular condition that requires medical evaluation even in the absence of symptoms.
Stages of Carotid Stenosis
Venous insufficiency progresses gradually. Recognizing early stages can help prevent complications.
- Often asymptomatic
- Early plaque formation
- Reduced blood flow
- Increased stroke risk
- High risk of stroke
- May require urgent intervention
- Blood flow fully blocked
- Medical emergency
What are the Risk Factors?
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing carotid stenosis:
Age
Risk increases after 60
Smoking
Damages arterial walls
High blood pressure
Accelerates plaque buildup
High cholesterol
Contributes to atherosclerosis
Diabetes
Affects vascular health
Family history
Genetic predisposition
Symptoms & Consequences
Carotid stenosis may be asymptomatic or cause:
Symptoms
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Temporary vision loss
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Possible Consequences
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Ischemic stroke
- Permanent neurological damage
- Loss of independence
When to Consult?
Immediate consultation is required if neurological symptoms occur, even if they resolve quickly.
Diagnosis of Carotid Stenosis
Early diagnosis allows timely intervention and stroke prevention.
Clinical Evaluation
Review of symptoms, medical history, and cardiovascular risk factors.
Doppler Ultrasound
A non-invasive test that measures blood flow and identifies arterial narrowing.
Advanced Imaging (if required)
CT angiography or MR angiography may be used for detailed assessment.
Why Early Treatment Matters
- Reduces stroke risk
- Preserves brain function
- Allows minimally invasive management
- Improves long-term outcomes
Prevention & Treatment
Treatment depends on stenosis severity and patient risk profile.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Quit smoking
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Medical management (antiplatelet therapy, statins)
- Lifestyle modification
- Surgical or interventional procedures when indicated
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery varies depending on treatment approach
- Most diagnostic procedures require no downtime
- Patients are monitored regularly with follow-up imaging
- Long-term management focuses on risk factor control
- Lifestyle changes play a critical role in preventing recurrence
Ongoing follow-up is essential for stroke prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is carotid stenosis life-threatening?
Yes, if untreated it significantly increases stroke risk.
Can carotid stenosis be reversed?
Plaque cannot be fully reversed, but progression can be slowed or stabilized.
Is carotid stenosis always symptomatic?
No, many patients have no symptoms until a stroke occurs.
How often should screening be done?
Frequency depends on risk factors and previous findings.
Is Doppler ultrasound painful?
No, it is non-invasive and painless.