The Circulatory System
Understanding how venous valves function is key to treating insufficiency.
In a healthy vein, small valves open to allow blood to flow toward the heart and close to prevent it from flowing backward. This mechanism fights gravity, especially in the legs.
When these valves weaken or fail, blood flows backward and pools in the veins (venous reflux). This increased pressure causes the veins to stretch, twist, and bulge, leading to varicose veins and insufficiency.
What is a Varicose Vein?
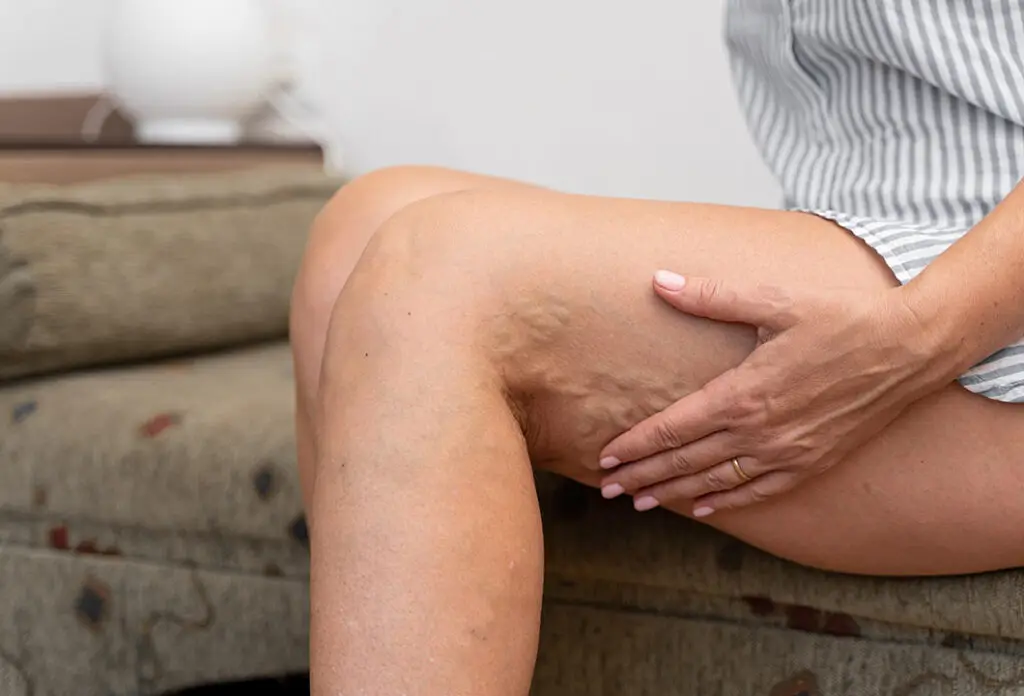
Types of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are dilated, tortuous, and elongated superficial veins. They are often blue or purple and bulge above the skin surface.
- Truncal Varicose Veins: Large, bulging veins usually from the saphenous system.
- Reticular Veins: Smaller blue or green veins below the skin surface.
- Spider Veins: Tiny red or purple veins right on the skin surface.
Stages of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Venous insufficiency progresses gradually. Recognizing early stages can help prevent complications.
Heaviness or tired legs. Mild discomfort after prolonged standing.
Small red or blue surface veins. Cosmetic concern with mild symptoms.
Enlarged, twisted veins. Aching, swelling, night cramps.
Persistent ankle and leg swelling. Skin tightness and discomfort.
Dark pigmentation (stasis dermatitis). Thickened or inflamed skin.
Non-healing wounds near ankles. Significant risk of infection and pain.
What are the Risk Factors?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing venous disease.
Heredity
Family history is the primary factor.
Lifestyle
Prolonged standing or sitting, obesity.
Age
Risk increases with age as valves wear.
Pregnancy
Increased blood volume and hormonal changes.
Gender
Women are more likely to be affected.
Heat
Exposure to excessive heat can dilate veins.
Symptoms & Consequences
Identifying the Signs of Venous Disease
Symptoms
- Heaviness in legs
- Pain or aching
- Swelling (Edema)
- Night cramps
- Itching (Pruritus)
Consequences
- Skin pigmentation
- Eczema
- Venous Ulcers
- Superficial Phlebitis
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
When to Consult?
Consult a specialist if you experience persistent pain, swelling, skin discoloration, or if veins become visibly swollen and warm to the touch. Early intervention prevents complications.
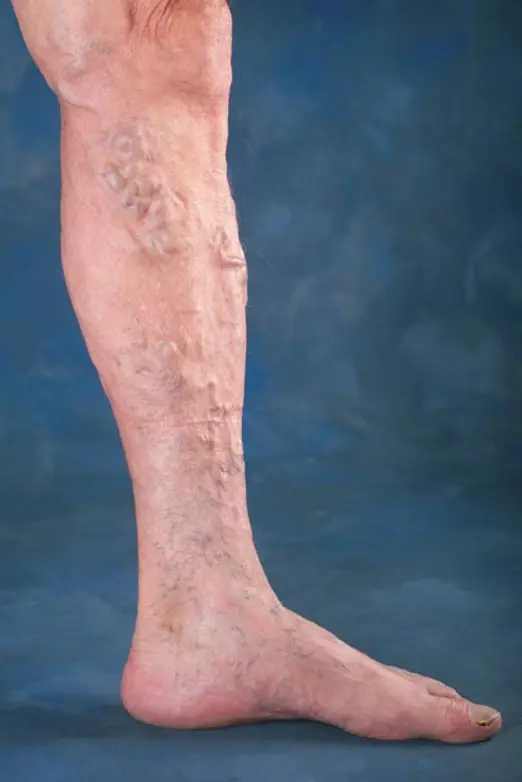
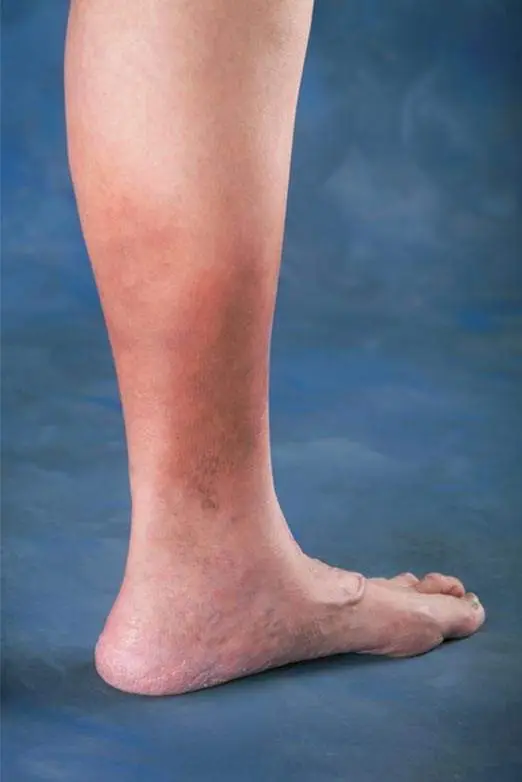
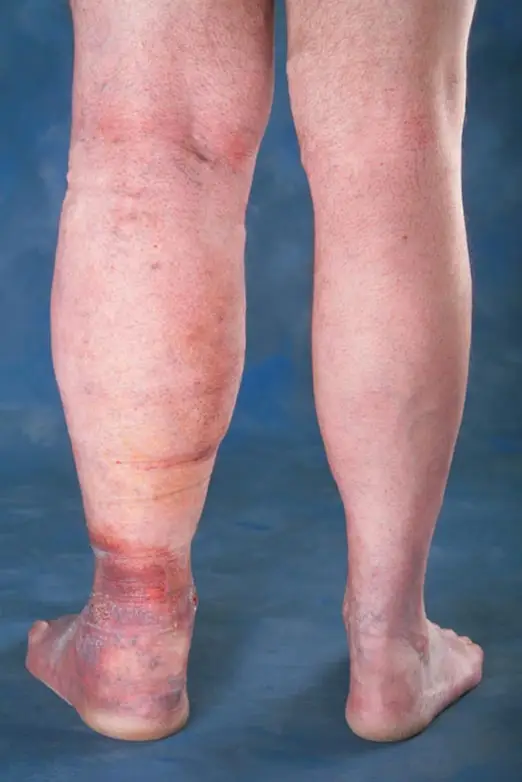
Diagnosis of Venous Insufficiency
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the severity and best treatment approach.
Clinical Examination
A physical assessment of the legs while standing and lying down to evaluate vein appearance and swelling.
Doppler Ultrasound
A painless imaging test that evaluates blood flow and identifies faulty vein valves or reflux.
Medical History Review
Assessment of symptoms, family history, occupation, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to venous disease.
Why Early Treatment Matters
- Chronic leg pain and swelling
- Venous eczema and hardening
- Increased risk of blood clots
- Skin discoloration and inflammation
- Formation of venous ulcers
Prevention & Treatment
Prevention
While not all cases can be prevented, certain habits reduce risk:
- Avoid prolonged standing/sitting
- Elevate legs whenever possible
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Regular walking or leg exercises
- Wear compression stockings
- Avoid tight clothing
- Sclerotherapy
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- VenaSeal / Echosclerosis
- Phlebectomy
Recovery and Aftercare
Most modern venous treatments are minimally invasive and allow rapid return to daily activities. Your specialist will provide personalized aftercare instructions.
- Walking encouraged immediately
- Mild discomfort or bruising may occur
- Compression stockings may be advised
- Resume normal activities: 24–48 hours
- Visible improvement: Over a few weeks
- Long-term relief with proper follow-up
Frequently Asked Questions
Is venous insufficiency a serious condition?
It can become serious if left untreated, potentially leading to ulcers, skin changes, and chronic pain. Early diagnosis is key.
Are treatments painful?
Most modern treatments are minimally invasive and performed under local anesthesia with little to no discomfort.
How long do results last?
Results are generally long-lasting, especially when combined with healthy lifestyle management and periodic follow-up care.
Can varicose veins return?
New veins may develop over time due to the progressive nature of the disease, but treated veins typically do not return.
Is treatment cosmetic or medical?
Venous insufficiency is a medical condition affecting circulation. While treatment improves appearance, the primary goal is often health and symptom relief.
